Kubernetes 1.34 – Top Security Enhancements 💪
Kubernetes v1.34 is coming soon, and it brings a rich batch of security upgrades –...

Apr 20, 2022
The first Kubernetes release of 2022 will be released on May 3rd. The new release, version 1.24, is full of enhancements, new features, and bug fixes.
We’ve written this post so you can adjust your Kubernetes resources, update infrastructure, and smoothly migrate to the new version. We’ve also grouped the changes with their respective Special Interest Groups (SIGs), so that you can focus on the interrelated topics at once.
Auth SIG is responsible for control of and access to the Kubernetes API, and there is an important new feature in the upcoming release: kubectl create token. Previously, you needed to scrape generated service account tokens with kubectl commands, similar to
kubectl get secret "$(kubectl get serviceaccount default -o jsonpath='{.secrets[0].name}')".
With the 1.24 release, you can easily create and retrieve the tokens. Using the new command in automation scripts and CI/CD pipelines will be practical.
Cloud Provider SIG focuses on developing and maintaining cloud provider integrations as extensions or add-ons. Add-ons are extensions that work with Kubernetes to add new functionalities. Cluster administrators configure and install the cluster add-ons to their Kubernetes clusters. In the 1.24 release, the cluster add-on for the Kubernetes dashboard is removed. If you create Kubernetes clusters and install the dashboard add-on, you need to revise your scripts and tooling. With the 1.24 release, it is suggested to install the Kubernetes dashboard by following the user guide.
The goal of Cluster Lifecycle SIG is to streamline Kubernetes cluster operations by focusing on configuration, creation, upgrades, downgrades, and removing the clusters in a cloud-native way. kubeadm is one of the tools that is maintained in the new version. You can use it to create minimum viable Kubernetes clusters by following best practices.
In the 1.24 release, there are two essential changes for kubeadm:
API Machinery SIG is responsible for the brain of the Kubernetes clusters, namely the control plane. There are a couple of changes in the upcoming release when it comes to marking some flags as deprecated and completely removing some already deprecated flags from kube-apiserver.
If you are using one of the following flags in your kube-apiserver deployments or cluster configuration tooling, it is time to change them immediately.
In addition, there are feature graduations and enhancements for the Kubernetes API:
Node SIG focuses on the components between the pods and host resources, such as computation. In other words, they are responsible for making sure that the pods are running as containers on the nodes. The 1.24 release includes significant changes to the two most critical components in the Node SIG area: container runtime and kubelet.
Docker has been in the Kubernetes landscape since the beginning of Kubernetes. When other container runtime options emerged, an initiative to make them standardized under Container Runtime Interface (CRI) was born. Then, dockershim was designed as a thin layer of software to use Docker as a container runtime.
dockershim was deprecated in version 1.20 and will be removed with the 1.24 release. This is a critical change mainly if you have a dependency on the Docker engine, such as running Docker commands in pods or relying on Docker registry configurations on the nodes. If you are using Docker as container runtime and still using dockershim, it’s time to remove the middleman and switch to a CRI-compatible runtime, as diagrammed below:
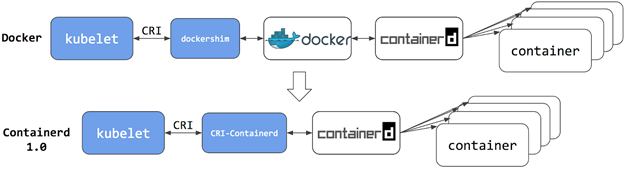
kubelet is the agent of Kubernetes running at each node and serves as the bridge between the Kubernetes API and node services. In the 1.24 version, the following flag changes will be released:
In addition, Dynamic Kubelet Configuration is a feature for dynamically changing the configuration of the kubelet instances running on the nodes. It works by employing a ConfigMap resource to define the kubelet configuration and using it as part of Node resources. This feature has been in the beta stage for a long time and has already been deprecated. In the 1.24 release, it is removed. If you are still using this feature, you should look into other options for updating kubelet and node configurations.
Testing SIG focuses on a comprehensive validation of Kubernetes by creating and running tests with various infrastructure options. In the new release, there are two critical changes:
$ curl -H "X-Forwarded-For: data" 172.17.0.2:8080/header?key=X-Forwarded-For data
Networking SIG is responsible for the interfaces, APIs, and components to expose the networking capabilities of Kubernetes clusters and workloads. In the 1.24 release, there is a critical bug fix from the SIG to resolve the duplicate port-opening issue in kube-proxy. kube-proxy is the network component that runs as a proxy in every Kubernetes node. Before the 1.24 release, when nodePortAddresses was empty, kube-proxy tried to open two ports triggered by IPv4ZeroCIDR and IPv6ZeroCIDR. The first attempt to open the port always succeeded, whereas the second attempt always failed. The fix ensures that nodeAddresses of proxies only contains the addresses for its IP family.
In addition, the 1.24 release includes an alpha feature for reserving service IP ranges for dynamic and static IP allocation. In Kubernetes, pods can communicate with each other using the Service resources. Kubernetes assigns IP addresses to the Service resources in two ways: dynamically from an IP range or statically with the user specification. However, while choosing a static IP, users can select an assigned IP, which will cause connectivity issues. The new feature will make it possible to separate two ranges for cluster IP assignment.
Scheduling SIG focuses on the assignment of pods to nodes, which is one of the core functionalities of Kubernetes. In the 1.24 release, there is a single essential change for the kube-scheduler. Insecure flags, such as –address and –port, have been removed. It is suggested to use –bind-address and –secure-port instead.
The first Kubernetes release of 2022 aims to make Kubernetes more secure and reliable. In addition, the enhancements on the infrastructure side, such as container runtime changes, will ensure that Kubernetes is up to date with the latest technological development in the cloud.
To learn more about the enhancements, check the Kubernetes blog and release notes.
To learn about the new version of Kubernetes v1.25, you can read here
Kubernetes v1.34 is coming soon, and it brings a rich batch of security upgrades –...
Kubernetes 1.33 marks another exciting milestone in the evolution of this widely adopted container orchestration...
Kubernetes continues to evolve its security posture with version 1.32, introducing several significant improvements in...