Three New High-Severity Vulnerabilities in runc: What You Need to Know
Within 24 hours, three new high-severity vulnerabilities were disclosed in runc, the low-level runtime that...

Jan 23, 2022
Linux maintainers disclosed a broadly available Linux kernel vulnerability – CVE-2022-0185 – that enables attackers to escape containers and get full control over the node. To be able to exploit this vulnerability, the attacker needs to be able to run code in the container and the container must have CAP_SYS_ADMIN privileges. Linux kernel and all major distro maintainers have released patches.
https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2022-0185
https://security-tracker.debian.org/tracker/CVE-2022-0185
https://ubuntu.com/security/CVE-2022-0185
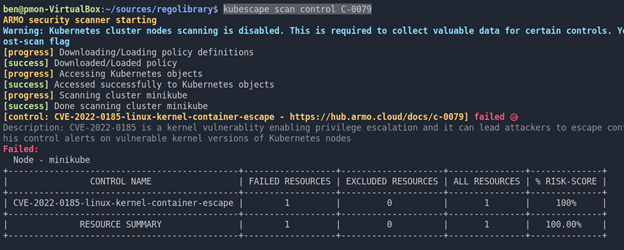
Kubescape scans and detects if your worker nodes are running the exploitable Linux version and if you have a pod with CAP_SYS_ADMIN capabilities, which indicated that someone can perform this attack on your cluster. You just need to run the ARMOBest framework in order to scan your clusters for this vulnerability.
kubescape scan control C-0079
The problem is an integer underflow problem in the “File System Context” component. Integer underflow happens when a subtraction over an unsigned integer variable falls below zero and the resulting calculation wraps around the integer’s max value instead of showing a negative value. When this underflow happens, a size check fails, and the invoker can write beyond the bounds of the allocated 4kb memory in the kernel space. Using this “unbound write” the attacker can change values in the kernel memory and, for example, add access to himself to any other process running on the same node.
The “File System Context” is used when the Linux kernel mounts a filesystem. This was replaced by “File Context API”, but for legacy support, part of the functionality was backported and the problem is in the handling of the legacy parameters. An unprivileged user local process (in case of unprivileged user namespaces enabled) or a process with CAP_SYS_ADMIN privileges can cause the invocation of the legacy code thus exploiting this vulnerability.
Credits to William Liu and Jamie Hill-Daniel for discovering the vulnerability.
The vulnerability was introduced in kernel 5.1 and patched in 5.16.2. You can mitigate completely the problem by patching to the latest version. Note, all major distributions released patches.
In case the kernel patching is not viable, there are different techniques that can partially mitigate the vulnerability.
Disabling unprivileged user namespaces means that an attacker will be limited to only containers/processes with CAP_SYS_ADMIN privileges (by default this is off for containers).
On most distributions, you can use this command to disable unprivileged namespaces
sysctl -w kernel.unprivileged_userns_clone = 0
On RedHat you can disable completely namespaces, but this is only relevant for kernels which does not need to run containers
# echo “user.max_user_namespaces=0” > /etc/sysctl.d/userns.conf
# sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/userns.conf
This vulnerability directly affects any containerized environment therefore Kubernetes users must follow up on this issue.
Besides the aforementioned mitigations, making sure that only necessary workloads that have CAP_SYS_ADMIN is paramount for preventing the exploitation of this problem.
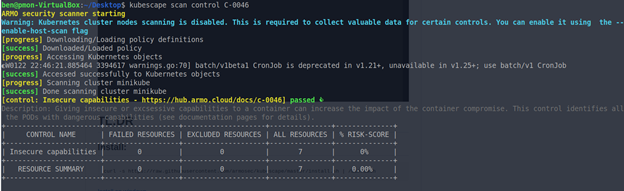
You can use Kubescape to detect such workloads by running C-0046 control over the cluster:
# kubescape scan control C-0046
Click here to learn more about Kubernetes security best practices

Within 24 hours, three new high-severity vulnerabilities were disclosed in runc, the low-level runtime that...

Hi there,We’ve just dropped a fresh batch of updates to help you cut through the...
Executive Summary On March 24, 2025, Wiz Research disclosed a series of critical vulnerabilities in...